The Hidden Code That Makes AI Choose Your Business
Most contractors think schema markup is some mysterious technical voodoo best left to developers. They’re half right—it is technical. But it’s also the single most underutilized weapon in local SEO, and the businesses that master it are quietly dominating AI-powered search results while their competitors remain invisible.
Here’s the brutal truth: when ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, or any other AI platform tries to understand your business, schema markup is like having someone whisper the answers directly into the AI’s ear. Without it, these systems struggle to extract basic facts from your website. With it, they instantly understand everything—what you do, where you serve, what you charge, when you’re available, and why customers love you.
This guide strips away the technical jargon and shows you exactly which schema markup matters for local businesses, how to implement it without being a coding expert, and the advanced strategies that separate businesses getting AI recommendations from those getting ignored.
What Schema Markup Actually Does (And Why AI Platforms Love It)
Think of your website as a conversation with a customer. You say “We’re open Monday through Friday, 8am to 6pm.” A human understands that instantly. But AI systems trying to figure out when you’re available have to parse that sentence, interpret it correctly, and extract structured data from unstructured text. They’re pretty good at it, but not perfect.
Schema markup eliminates the guesswork. It’s like providing a cheat sheet that says: “BUSINESS_HOURS: Monday-Friday, 08:00-18:00” in language AI systems understand natively. Instead of interpreting your content, they can just read the structured data directly.
Why this matters more than ever:
- AI Overviews and ChatGPT generate responses by synthesizing information from multiple sources. When they encounter schema markup, extraction becomes instant and accurate. Your business hours, services, prices, service areas, and reviews all become immediately accessible data points that AI can confidently cite.
- Voice assistants pulling business recommendations need structured information. Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant all rely heavily on schema to understand business attributes quickly. Well-implemented schema dramatically increases your chances of being recommended.
- Featured snippets and rich results in Google still matter tremendously. Schema is what powers star ratings in search results, FAQ expandables, how-to rich results, and business information panels. These enhanced listings capture attention and clicks.
The Core Schema Types Every Local Business Needs
Forget about implementing dozens of schema types. Start with these five foundational elements that deliver the biggest impact for local service businesses.
LocalBusiness Schema: Your Digital Identity Card
LocalBusiness schema is the foundation—it tells search engines and AI platforms the basic facts about your business that they’ll reference constantly.
Critical properties to include:
- Business name exactly as it appears everywhere else
- Complete physical address with street, city, state, ZIP
- Primary phone number that actually reaches your business
- Business email address for contact
- Website URL pointing to your homepage
- Latitude and longitude coordinates for precise location
- Logo image URL at high resolution
- Business hours for each day of the week
- Price range indicator ($$, $$$, etc.)
- Payment methods accepted
- Service area descriptions or geographic coverage
Advanced LocalBusiness properties that differentiate you:
- Use specific business subtypes instead of generic LocalBusiness. If you’re an HVAC contractor, use “HVACBusiness” as your type. Electricians should use “Electrician,” plumbers use “Plumber,” and so on. These specific types help AI platforms match you to precise service queries.
- Include founding date to establish longevity. “Founded in 1987” becomes a trust signal that AI platforms can reference when recommending established, reliable businesses.
- Add parent organization if you’re part of a franchise or larger company. This connection helps AI understand your business relationships and potentially inherit credibility from the parent brand.
- List multiple phone numbers with specific ContactPoint schemas. Designate one for customer service, another for emergency calls, another for estimates. This specificity helps AI route customers appropriately.
Service Schema: Telling AI Exactly What You Do
Generic service descriptions confuse AI systems trying to match businesses to specific customer needs. Service schema provides granular clarity about every service you offer.
How to structure service schema effectively:
- Create separate Service schema entries for each distinct service. Don’t lump “HVAC services” into one schema—break it into furnace repair, AC installation, duct cleaning, maintenance contracts, emergency service, and every other distinct offering.
- Include service type classification using industry-standard categories. Match your services to recognized classifications that AI systems already understand.
- Describe service areas geographically for each service. Maybe you do routine maintenance citywide but only emergency service within a smaller radius. Specify this distinction.
- Add aggregate rating specifically for each service if you have service-specific reviews. Overall business rating matters, but service-specific ratings help AI make precise recommendations.
Example service differentiation:
Instead of one “Plumbing Services” schema entry, create distinct schemas for:
- Emergency plumbing repair (24/7, all service areas, premium pricing)
- Drain cleaning (standard hours, residential and commercial)
- Water heater installation (scheduled appointments, residential only)
- Leak detection (specialized service, requires scheduling)
- Sewer line repair (excavation services, requires permits)
- Fixture installation (remodels and upgrades, by appointment)
Learn more about marketing your plumbing services online.
This granularity helps AI systems recommend your specific service that matches what the customer actually needs.
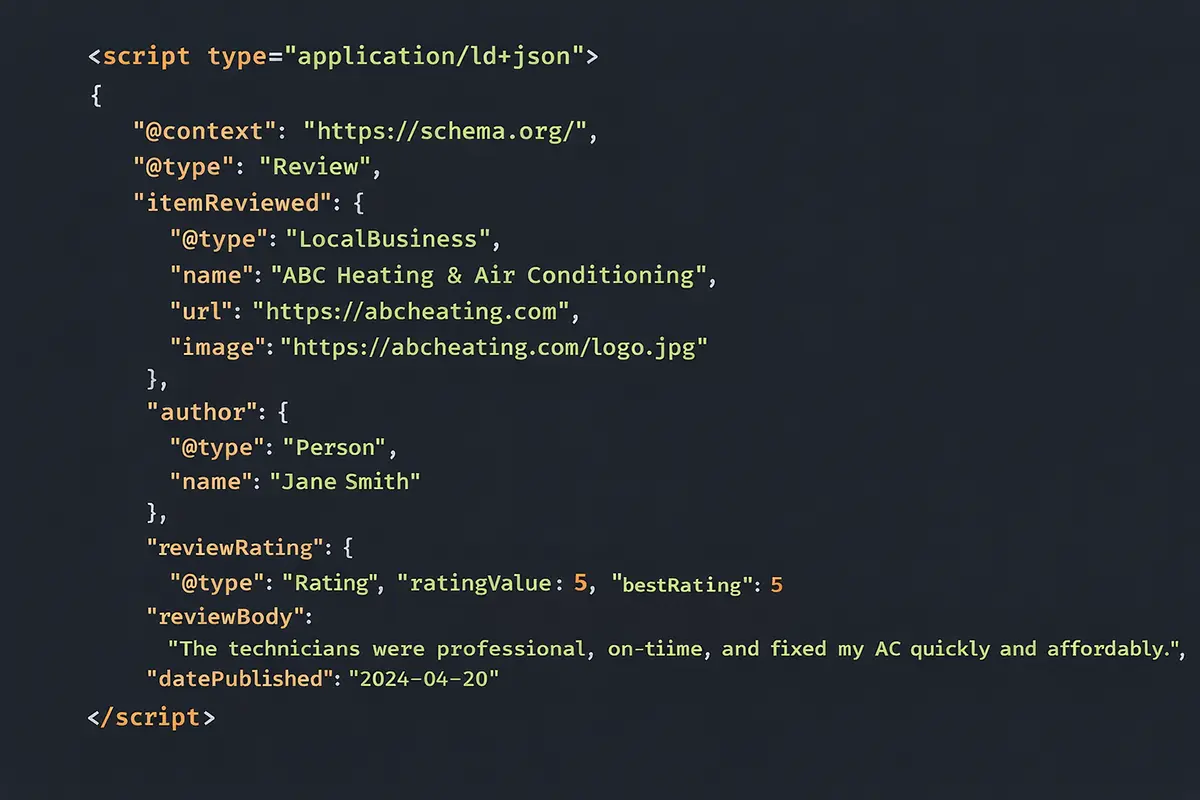
Review Schema: Showcasing Social Proof AI Can Read
Reviews scattered across your website in testimonial sections are invisible to AI without proper markup. Review schema makes every testimonial machine-readable and citable.
Implementing individual review markup:
Mark up every testimonial on your site with Review schema including the reviewer’s name, review body text, rating value, and date published. This transforms static testimonials into structured data AI can reference.
Include reviewer location when possible. Reviews from customers in neighborhoods you serve carry extra weight for local queries.
Add specific service mentions within review text. When marking up reviews, ensure the review text mentions specific services, not just generic praise. “Great HVAC service” is okay, but “They replaced our furnace in one day and explained everything clearly” gives AI specific information to work with.
Aggregate rating schema for overall reputation:
Combine all your reviews into an aggregateRating schema showing total review count and average star rating. This summary data appears in search results and provides AI with instant reputation assessment.
Update aggregate ratings regularly as new reviews come in. Stale rating data undermines trust—keep this current.
Segment aggregate ratings by service type if possible. Overall 4.8 stars is excellent, but showing 4.9 stars specifically for emergency service helps AI recommend you confidently for urgent situations.
FAQ Schema: Answering Questions Before They’re Asked
FAQ schema turns your question-and-answer content into structured data that AI platforms can instantly extract and cite when answering user queries.
Strategic FAQ implementation:
Mark up every FAQ section on your site with proper FAQPage schema. Include the complete question text and complete answer text for each Q&A pair.
Use questions exactly as customers phrase them. “What should I do if my furnace stops working?” not “Furnace Troubleshooting Guidelines.” Natural question phrasing matches how users query AI systems.
Provide complete answers within the schema. Don’t just mark up a teaser with “Click to read more”—include the full answer text so AI can extract and cite it directly.
FAQ topics that perform exceptionally well:
- Emergency situation guidance (What counts as an emergency? What do I do first?)
- Cost and pricing questions (How much does typical service cost? What affects pricing?)
- Service process questions (How long does installation take? What should I expect?)
- Qualification questions (Are you licensed? Do you have insurance?)
- Availability questions (Do you offer emergency service? What are your hours?)
- Service area questions (Do you serve my neighborhood? How far do you travel?)
How To Schema: Demonstrating Expertise Through Process
HowTo schema structures instructional content into step-by-step processes that AI systems can understand and reference when users need guidance.
When to use HowTo schema:
Apply HowTo schema to any content teaching customers a process: troubleshooting common problems, preparing for service visits, performing basic maintenance, choosing between service options, or understanding what to expect during service.
HowTo schema structure that works:
Break processes into clear sequential steps numbered appropriately. Each step should include step text, and optionally an image showing that step and estimated time for completion.
Include tools or materials needed for the process upfront. This helps AI understand prerequisites and determine if the process is appropriate for the user’s situation.
Add total time estimate for the entire process. Users asking AI for help often want to know time commitment before starting.
Example HowTo implementation for contractors:
“How to Prepare Your Home for an HVAC Installation” becomes a structured HowTo with steps like:
- Clear the area around your current system (30 minutes, requires moving furniture)
- Ensure clear path from entry to installation location (15 minutes)
- Protect floors with drop cloths if you have them (10 minutes)
- Secure pets in a separate area (5 minutes)
- Designate parking area for service vehicle (inform neighbors if needed)
This structure helps AI walk users through preparation while positioning you as thorough and professional.
Advanced Schema Strategies That Create Competitive Moats
Basic schema implementation gets you in the game. Advanced strategies create separation from competitors who stop at the basics.
Geographic Schema Layering for Service Area Domination
Most businesses add one address to their LocalBusiness schema and call it done. Advanced strategy involves layering geographic schema throughout your site to dominate every area you serve.
Multi-location schema architecture:
If you have multiple physical locations, implement separate LocalBusiness schema for each with unique addresses, phone numbers, and operating hours. Don’t duplicate identical schemas with just address changes—each location should have genuinely distinct information.
For single-location businesses serving broad areas, use areaServed property extensively. List every city, neighborhood, and ZIP code you serve. The more specific your geographic schema, the better AI systems match you to location-based queries.
Create location-specific landing pages with embedded LocalBusiness schema showing that address as serviceArea. Even if you don’t have offices in Squirrel Hill, your “Services in Squirrel Hill” page can include schema showing you actively serve that area.
Radius-based service area schema:
Some services have radius-based coverage. Use GeoCircle schema to specify your service area as a radius from your location. Emergency services might be 15 miles, routine service might be 30 miles—specify these distinctions.
Combine radius schema with explicit city listings. “We serve all locations within 20 miles of our Oakland office, including Squirrel Hill, Shadyside, East Liberty, Bloomfield…” gives AI both structured (radius) and explicit (city names) geographic data.
Time-Sensitive Schema for Availability Signaling
Availability drives AI recommendations for service businesses. Advanced time schema ensures AI platforms know exactly when you’re available and how quickly you respond.
Operating hours sophistication:
Go beyond basic business hours. Use specialOpeningHoursSpecification for holiday hours, seasonal variations, and special circumstances. Mark up that you’re closed Thanksgiving but open the day after, closed Christmas week but open New Year’s Day.
Specify different hours for different services. Your office might be open 8am-5pm, but emergency service is 24/7. Create distinct openingHoursSpecification entries for different service types.
Response time schema:
While not officially in Schema.org vocabulary, you can use additionalProperty to add custom properties like “emergencyResponseTime” with values like “Under 2 hours” or “Same-day service available.” AI systems increasingly parse these custom properties for additional context.
Pricing Schema That Builds Trust Without Limiting Flexibility
Contractors hesitate to publish pricing, fearing they’ll lock themselves into fixed rates or lose price-sensitive customers. Strategic pricing schema provides guidance without commitment.
Transparent pricing approaches:
- Use priceRange property ($$, $$$, etc.) for general positioning. This gives AI a sense of whether you’re budget, mid-range, or premium without specific numbers.
- Implement Offer schema for specific services where you can provide clear pricing. “Furnace tune-up: $129” becomes structured data AI can cite. Services with variable pricing can use priceRange within Offer schema.
- Add priceSpecification with pricing factors explained. “Pricing depends on system size, complexity, and parts required. Service call fee $89 applies to diagnostic visit” becomes structured information helping set expectations.
Pricing schema that converts:
- Include eligibility requirements for special pricing in Offer schema. “Senior discount available” or “First-time customer special” with specific discount amounts helps AI recommend you to eligible customers.
- Mark up financing options as PaymentMethod. Accepting credit cards is standard, but advertising that you offer financing with approved credit differentiates you in AI recommendations.
Schema Implementation Without Touching Code
Most contractors freeze when they hear “implement schema markup” because they imagine writing complex code. Modern tools make implementation surprisingly accessible.
Plugin-based implementation for WordPress:
Rank Math, Yoast SEO, and Schema Pro all offer visual schema builders. You fill out forms, the plugin generates proper schema code. These handle LocalBusiness, Service, FAQ, and Review schema with minimal technical knowledge required.
Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper:
Google provides a free tool where you highlight content on your page and tag it as specific schema types. The tool generates the code, which you or your developer paste into your site. It’s tedious for large implementations but perfect for learning and small-scale deployment.
JSON-LD generators:
Numerous online tools generate schema markup in JSON-LD format (the format Google recommends). You input your business information, the tool outputs code, you add it to your site header. Search “schema markup generator for local business” and test several.
Schema validation is non-negotiable:
After implementing schema, always validate it using Google’s Rich Results Test and Schema Markup Validator. These tools show you exactly what search engines see and flag errors preventing proper parsing. Fix all errors and warnings before considering implementation complete.
Common Schema Mistakes That Torpedo Your Efforts
Schema markup isn’t forgiving—small mistakes can invalidate everything, making your effort worthless or even counterproductive.
Critical mistakes to avoid:
- Mismatching visible content and schema data. If your website says you’re open 9-5 but schema says 8-6, AI systems detect the inconsistency and may ignore all your schema. Schema must match visible content exactly.
- Implementing schema on pages without relevant content. Don’t add Service schema for furnace repair to your about page. Schema goes on the page with corresponding content—Service schema on service pages, FAQ schema on FAQ sections, Review schema where testimonials appear.
- Using deprecated or incorrect schema types. Schema.org updates regularly. Using outdated property names or obsolete schema types can cause validation failures. Check current Schema.org documentation.
- Over-marking content inappropriately. Don’t mark promotional content as FAQ or review schema. Only mark genuine customer questions, actual customer reviews, and real instructional content. Misuse can result in manual penalties.
Advanced local schema markup isn’t about gaming systems—it’s about clear communication with AI platforms trying to understand and recommend your business. By implementing comprehensive, accurate schema that reflects your genuine expertise and service quality, you make it exponentially easier for AI to choose you when customers need help.